Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.maskers.MultiNiftiMasker#
- class nilearn.maskers.MultiNiftiMasker(mask_img=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, standardize_confounds=True, detrend=False, high_variance_confounds=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='background', mask_args=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0, n_jobs=1, verbose=0)[source]#
Class for masking of Niimg-like objects.
MultiNiftiMasker is useful when dealing with image sets from multiple subjects. Use case: integrates well with decomposition by MultiPCA and CanICA (multi-subject models)
- Parameters
- mask_imgNiimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Mask of the data. If not given, a mask is computed in the fit step. Optional parameters can be set using mask_args and mask_strategy to fine tune the mask extraction.
- smoothing_fwhm
float, optional. If
smoothing_fwhmis notNone, it gives the full-width at half maximum in millimeters of the spatial smoothing to apply to the signal.- standardize{False, True, ‘zscore’, ‘psc’}, optional
Strategy to standardize the signal. ‘zscore’: the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. ‘psc’: Timeseries are shifted to zero mean value and scaled to percent signal change (as compared to original mean signal). True : the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. False : Do not standardize the data. Default=False.
- standardize_confoundsboolean, optional
If standardize_confounds is True, the confounds are z-scored: their mean is put to 0 and their variance to 1 in the time dimension. Default=True.
- high_variance_confoundsboolean, optional
If True, high variance confounds are computed on provided image with
nilearn.image.high_variance_confoundsand default parameters and regressed out. Default=False.- detrendboolean, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. Default=False.
- low_passNone or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- high_passNone or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- t_rfloat, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- target_affine3x3 or 4x4 matrix, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
- target_shape3-tuple of integers, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
- mask_strategy{‘background’, ‘epi’, ‘whole-brain-template’,’gm-template’, ‘wm-template’}, optional
The strategy used to compute the mask:
‘background’: Use this option if your images present a clear homogeneous background.
‘epi’: Use this option if your images are raw EPI images
‘whole-brain-template’: This will extract the whole-brain part of your data by resampling the MNI152 brain mask for your data’s field of view.
Note
This option is equivalent to the previous ‘template’ option which is now deprecated.
‘gm-template’: This will extract the gray matter part of your data by resampling the corresponding MNI152 template for your data’s field of view.
New in version 0.8.1.
‘wm-template’: This will extract the white matter part of your data by resampling the corresponding MNI152 template for your data’s field of view.
New in version 0.8.1.
Note
Depending on this value, the mask will be computed from
nilearn.masking.compute_multi_background_mask,nilearn.masking.compute_multi_epi_mask, ornilearn.masking.compute_multi_brain_mask.Default is ‘background’.
- mask_argsdict, optional
If mask is None, these are additional parameters passed to masking.compute_background_mask or masking.compute_epi_mask to fine-tune mask computation. Please see the related documentation for details.
- dtype{dtype, “auto”}, optional
Data type toward which the data should be converted. If “auto”, the data will be converted to int32 if dtype is discrete and float32 if it is continuous.
- memoryinstance of joblib.Memory or string, optional
Used to cache the masking process. By default, no caching is done. If a string is given, it is the path to the caching directory.
- memory_levelinteger, optional
Rough estimator of the amount of memory used by caching. Higher value means more memory for caching. Default=0.
- n_jobsinteger, optional
The number of CPUs to use to do the computation. -1 means ‘all CPUs’, -2 ‘all CPUs but one’, and so on. Default=1.
- verboseinteger, optional
Indicate the level of verbosity. By default, nothing is printed. Default=0.
See also
nilearn.image.resample_imgimage resampling
nilearn.masking.compute_epi_maskmask computation
nilearn.masking.apply_maskmask application on image
nilearn.signal.cleanconfounds removal and general filtering of signals
- Attributes
- `mask_img_`nibabel.Nifti1Image object
The mask of the data.
- `affine_`4x4 numpy.ndarray
Affine of the transformed image.
- __init__(mask_img=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, standardize_confounds=True, detrend=False, high_variance_confounds=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='background', mask_args=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0, n_jobs=1, verbose=0)[source]#
- fit(imgs=None, y=None)[source]#
Compute the mask corresponding to the data
- Parameters
- imgslist of Niimg-like objects
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Data on which the mask must be calculated. If this is a list, the affine is considered the same for all.
- transform_imgs(imgs_list, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, copy=True, n_jobs=1)[source]#
Prepare multi subject data in parallel
- Parameters
- imgs_listlist of Niimg-like objects
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html List of imgs file to prepare. One item per subject.
- confoundslist of confounds, optional
List of confounds (2D arrays or filenames pointing to CSV files or pandas DataFrames). Must be of same length than imgs_list.
- sample_masklist of sample_mask, optional
List of sample_mask (1D arrays) if scrubbing motion outliers. Must be of same length than imgs_list.
New in version 0.8.0.
- copyboolean, optional
If True, guarantees that output array has no memory in common with input array. Default=True.
- n_jobsinteger, optional
The number of cpus to use to do the computation. -1 means ‘all cpus’. Default=1.
- Returns
- region_signalslist of 2D numpy.ndarray
List of signal for each element per subject. shape: list of (number of scans, number of elements)
- transform(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None)[source]#
Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
- Parameters
- imgslist of Niimg-like objects
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Data to be preprocessed
- confoundsCSV file path or 2D array or pandas DataFrame, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the corresponding documentation for details.
- sample_masklist of sample_mask, optional
List of sample_mask (1D arrays) if scrubbing motion outliers. Must be of same length than imgs_list.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- data{list of numpy arrays}
preprocessed images
- fit_transform(X, y=None, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, **fit_params)[source]#
Fit to data, then transform it
- Parameters
- XNiimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html
- ynumpy array of shape [n_samples], optional
Target values.
- confoundslist of confounds, optional
List of confounds (2D arrays or filenames pointing to CSV files). Must be of same length than imgs_list.
- sample_masklist of sample_mask, optional
List of sample_mask (1D arrays) if scrubbing motion outliers. Must be of same length than imgs_list.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- X_newnumpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new]
Transformed array.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- inverse_transform(X)[source]#
Transform the 2D data matrix back to an image in brain space.
- Parameters
- XNiimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html
- Returns
- imgTransformed image in brain space.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- transform_single_imgs(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, copy=True)[source]#
Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
- Parameters
- imgs3D/4D Niimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Images to process. It must boil down to a 4D image with scans number as last dimension.
- confoundsCSV file or array-like or pandas DataFrame, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)- sample_maskAny type compatible with numpy-array indexing, optional
shape: (number of scans - number of volumes removed, ) Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension to perform scrubbing (remove volumes with high motion) and/or non-steady-state volumes. This parameter is passed to signal.clean.
- copyBoolean, optional
Indicates whether a copy is returned or not. Default=True.
- Returns
- region_signals2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each voxel inside the mask. shape: (number of scans, number of voxels)
Examples using nilearn.maskers.MultiNiftiMasker#

Encoding models for visual stimuli from Miyawaki et al. 2008
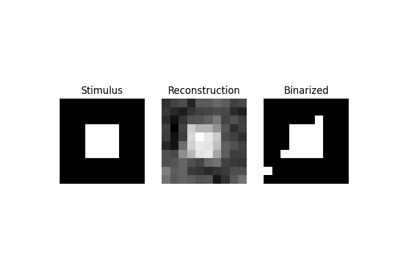
Reconstruction of visual stimuli from Miyawaki et al. 2008