Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.plotting.plot_prob_atlas#
- nilearn.plotting.plot_prob_atlas(maps_img, bg_img=<MNI152Template>, view_type='auto', threshold='auto', linewidths=2.5, cut_coords=None, output_file=None, display_mode='ortho', figure=None, axes=None, title=None, annotate=True, draw_cross=True, black_bg='auto', dim='auto', colorbar=False, cmap=<matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap object>, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=0.7, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot the probabilistic atlases onto the anatomical image by default MNI template
- Parameters
- maps_imgNiimg-like object or the filename
4D image of the probabilistic atlas maps.
- bg_imgNiimg-like object, optional
See input_output. The background image to plot on top of. If nothing is specified, the MNI152 template will be used. To turn off background image, just pass “bg_img=False”. Default=MNI152TEMPLATE.
New in version 0.4.0.
- view_type{‘auto’, ‘contours’, ‘filled_contours’, ‘continuous’}, optional
By default view_type == ‘auto’, means maps will be displayed automatically using any one of the three view types. The automatic selection of view type depends on the total number of maps. If view_type == ‘contours’, maps are overlaid as contours If view_type == ‘filled_contours’, maps are overlaid as contours along with color fillings inside the contours. If view_type == ‘continuous’, maps are overlaid as continuous colors irrespective of the number maps. Default=’auto’.
- thresholda str or a number, list of str or numbers, optional
This parameter is optional and is used to threshold the maps image using the given value or automatically selected value. The values in the image above the threshold level will be visualized. The default strategy, computes a threshold level that seeks to minimize (yet not eliminate completely) the overlap between several maps for a better visualization. The threshold can also be expressed as a percentile over the values of the whole atlas. In that case, the value must be specified as string finishing with a percent sign, e.g., “25.3%”. If a single string is provided, the same percentile will be applied over the whole atlas. Otherwise, if a list of percentiles is provided, each 3D map is thresholded with certain percentile sequentially. Length of percentiles given should match the number of 3D map in time (4th) dimension. If a number or a list of numbers, the given value will be used directly to threshold the maps without any percentile calculation. If None, a very small threshold is applied to remove numerical noise from the maps background.
- linewidths
float, optional Set the boundary thickness of the contours. Only reflects when
view_type=contours. Default=2.5.- cut_coordsNone, a
tupleoffloat, orint, optional The MNI coordinates of the point where the cut is performed.
If
display_modeis ‘ortho’ or ‘tiled’, this should be a 3-tuple:(x, y, z)For
display_mode == 'x', ‘y’, or ‘z’, then these are the coordinates of each cut in the corresponding direction.If
Noneis given, the cuts are calculated automatically.If
display_modeis ‘mosaic’, and the number of cuts is the same for all directions,cut_coordscan be specified as an integer. It can also be a length 3 tuple specifying the number of cuts for every direction if these are different.
Note
If
display_modeis ‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’,cut_coordscan be an integer, in which case it specifies the number of cuts to perform.- output_file
str, or None, optional The name of an image file to export the plot to. Valid extensions are .png, .pdf, .svg. If
output_fileis not None, the plot is saved to a file, and the display is closed.- display_mode{‘ortho’, ‘tiled’, ‘mosaic’,’x’,’y’, ‘z’, ‘yx’, ‘xz’, ‘yz’}, optional
Choose the direction of the cuts:
‘x’: sagital
‘y’: coronal
‘z’: axial
‘ortho’: three cuts are performed in orthogonal directions
‘tiled’: three cuts are performed and arranged in a 2x2 grid
‘mosaic’: three cuts are performed along multiple rows and columns
Default=’ortho’.
- figure
int, ormatplotlib.figure.Figure, or None, optional Matplotlib figure used or its number. If
Noneis given, a new figure is created.- axes
matplotlib.axes.Axes, or 4 tupleoffloat: (xmin, ymin, width, height), optional The axes, or the coordinates, in matplotlib figure space, of the axes used to display the plot. If
None, the complete figure is used.- title
str, or None, optional The title displayed on the figure. Default=None.
- annotate
bool, optional If
annotateisTrue, positions and left/right annotation are added to the plot. Default=True.- draw_cross
bool, optional If
draw_crossisTrue, a cross is drawn on the plot to indicate the cut position. Default=True.- black_bg
bool, or ‘auto’, optional If
True, the background of the image is set to be black. If you wish to save figures with a black background, you will need to pass facecolor=’k’, edgecolor=’k’ tomatplotlib.pyplot.savefig. Default=’auto’.- dim
float, or ‘auto’, optional Dimming factor applied to background image. By default, automatic heuristics are applied based upon the background image intensity. Accepted float values, where a typical span is between -2 and 2 (-2 = increase contrast; 2 = decrease contrast), but larger values can be used for a more pronounced effect. 0 means no dimming. Default=’auto’.
- cmap
matplotlib.colors.Colormap, orstr, optional The colormap to use. Either a string which is a name of a matplotlib colormap, or a matplotlib colormap object. Default=`plt.cm.gist_rainbow`.
- colorbar
bool, optional If
True, display a colorbar on the right of the plots. Default=False.- vmin
float, optional Lower bound of the colormap. If
None, the min of the image is used. Passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.imshow.- vmax
float, optional Upper bound of the colormap. If
None, the max of the image is used. Passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.imshow.- alphafloat between 0 and 1, optional
Alpha sets the transparency of the color inside the filled contours. Default=0.7.
See also
nilearn.plotting.plot_roiTo simply plot max-prob atlases (3D images)
Examples using nilearn.plotting.plot_prob_atlas#
Visualizing a probabilistic atlas: the default mode in the MSDL atlas
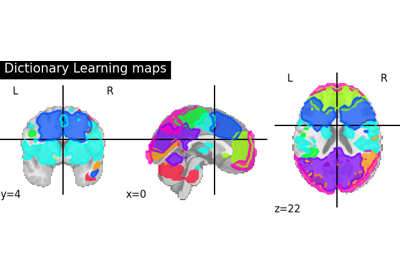
Deriving spatial maps from group fMRI data using ICA and Dictionary Learning
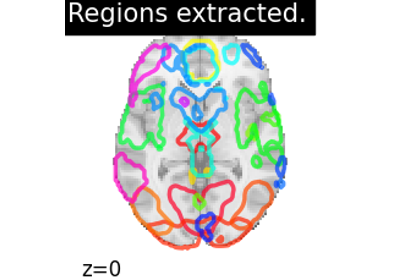
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes
Regions Extraction of Default Mode Networks using Smith Atlas